DECISION MAKING STRUCTURES
‘C’ language provides different control structures for decision making- like if statement, if….else statement, else-if-ladder.
Ø
If statement –
This is the simplest statement which checks a
condition. If the condition is true then the statement are executed, otherwise
they are not executed.
The syntax of if statement is -
If(condition)
{
Statement(s) ;
}
If there are more
than one statement to be executed then they are put within { } symbols.
Ø
If…else Statement –
In certain cases, we
want to execute one set of statement, if condition is satisfied, and other set
of statements if condition is false. In that case we can use if…else statement.
The syntax of if statement is -
If(condition)
{
Statement(s)1 ;
}
Else
{
Statement(s)2 ;
}
If condition is TRUE, then
statement(s)1 are executed, otherwise statement(s)2 are executed.
· For Example –
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void
main()
{
Int a,b;
clrscr();
scanf(“%d”,&a);
scanf(“%d”,&b);
if(a > b)
{
printf(“a is greater than
b”);
}
else
{
printf(“b is greater than a”);
}
getch();
}
Ø
Nested if Statement –
For complex problems we need to check more than one condition. The if statement can be used inside another if statement. This type of use of if statement is called as nested if statement. The nesting can be up to any level.
·
For Example –
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void
main()
{
int a,b,c;
clrscr();
scanf(“%d”,&a);
scanf(“%d”,&b);
scanf(“%d”,&c);
if(a > b)
{
if(a > c)
{
printf(“a is
greater than b and c”);
}
else
{
printf(“c is
greater than a and b”);
}
}
else
{
if(b > c)
{
printf(“b is
greater than c”);
}
else
{
printf(“a is
greater than b”);
}
}
getch();
}
Ø
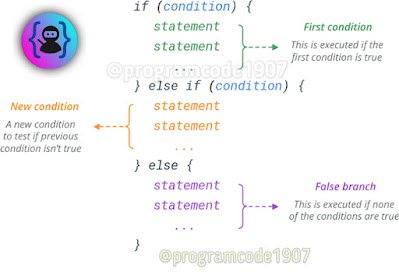
If…else…if Ladder (Multiple if…else) Statement –
The two-way decision provided by if…else
statement is not sufficient when we are having many choice, ‘C’ language
provides a multiple if…else statement for that purpose.
The syntax of if-else-ladder is –
if(condition1)
{
Statement(s)1
;
}
else
if(condition2)
{
Statement(s)2 ;
}
.
.
.
else
if(condition N)
{
Statement(s)N ;
}
else
{
Default_statement(s);
}
From the syntax, it is very clear that
only set of statement(s) will be executed, depending on the condition being
TRUE.



0 Comments
If You have any query, Please let me know..